What is sun overexposure?
When a person spends an extended amount of time in direct sunlight without taking proper precautions, such as wearing protective clothing or applying sunscreen, they may be at risk for sun overexposure.
Overexposure to the sun's UV rays can lead to a number of serious health problems, including skin cancer and premature aging etc.
The human body has a natural defense against overexposure to the sun's UV rays called melanin.
However, people with light skin are at an increased risk of getting sunburns and developing skin cancer because they do not produce enough melanin.
A person can get UV rays overexposure in the following ways:
- Spending too much time outside in the sun.
- Using tanning beds.
- Getting a tan through self-tanning lotions, creams, and sprays.

Why it is dangerous to overexpose to the Sun
The Sun is a powerful and life-giving star, but it can also be dangerous if we are not careful.
Overexposure to the Sun can lead to skin cancer, which is the most common type of cancer in the United States.
The Sun emits three types of radiation: UVA rays, UVB rays, and UVC rays. The first two types are what cause sunburns and skin cancer.
UVC rays are filtered out by Earth's atmosphere before they reach the ground.
Solar radiation refers to the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun. This includes visible light, ultraviolet light, infrared radiation, and X-rays.
Sun overexposure can cause premature aging of the skin or hair loss.
This is because sun overexposure can damage the DNA in skin cells or hair follicles, causing them to age prematurely or fall out.
For example, sun overexposure can cause wrinkles, sagging skin, and brown spots. In extreme cases, it can also lead to skin cancer.
Side effects of Sun overexposure
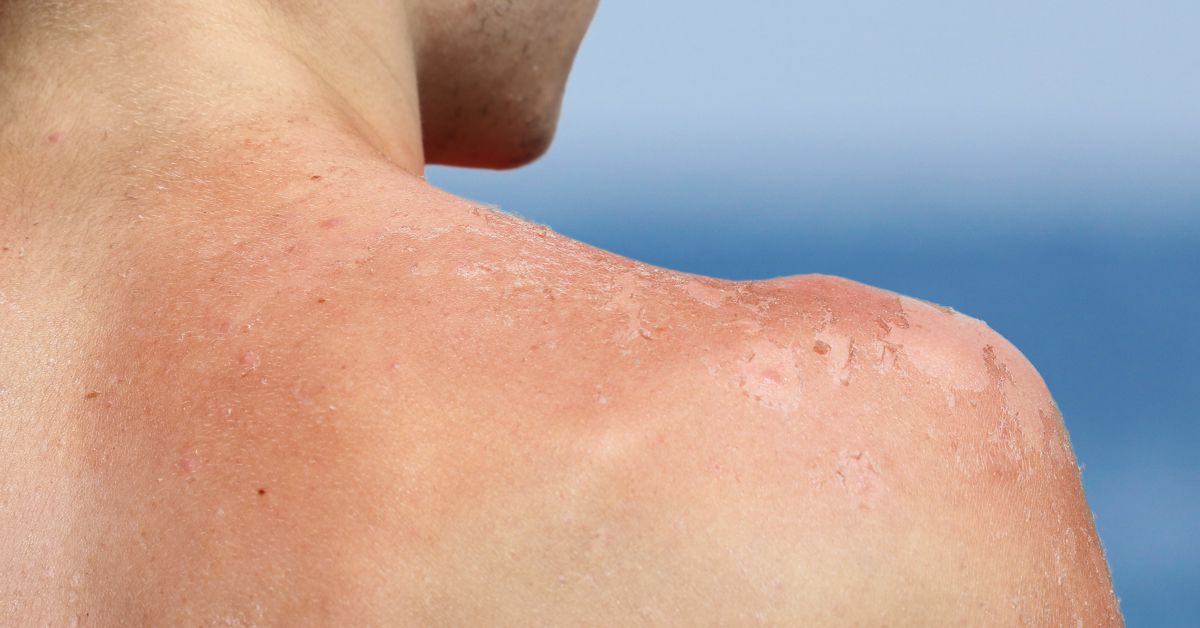
The side effects of sun overexposure are not limited to skin cancer. There are many other issues that can arise from too much exposure to the sun, including eye problems, dry and peeling skin, and even premature aging.
In this section we will list some of the most common side effects of overexposure to the sun.
- Skin cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the skin cells, usually due to too much exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or artificial sources like tanning beds. Skin cancer can be either non-melanoma or melanoma. Non-melanoma skin cancers are more common, but melanoma skin cancers are more likely to spread to other parts of the body and be fatal.
- Too much exposure to UV radiation can also lead to eye problems such as cataracts and macular degeneration. These conditions can result in poor vision or even blindness.
- Dry and peeling skin is a common problem for people who spend too much time in the sun without proper protection. This can be a particular issue during hot weather, when the sun's rays are more intense.
- Premature aging is another potential consequence of spending too much time in the sun without protection. This is especially true for people with fair skin, as they are more susceptible to damage from the sun's UV rays. Spending too much time in the sun can lead to fine lines and wrinkles, as well as dryness and pigmentation issues.
Sun overexposure symptoms
Suffering from sun overexposure is one of the most common summertime ailments. The sun can cause skin damage, heat stroke, and even blindness.
There is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the symptoms of sun overexposure, as they vary depending on the individual.
However, there are some general symptoms that you should be aware of:
- A headache
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue
- Eye irritation
- Redness and inflammation
- Fever
- Skin peeling after a few days

The importance of Sunscreen
Sunscreen is the most important product to have in your arsenal.
It is important because it protects your skin from harmful UV rays that cause skin cancer, age spots and wrinkles.
It is important to apply sunscreen before going outside, especially if you are planning on being outdoors for an extended period of time.
You should also reapply sunscreen every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
Sunscreen is not just important because it protects you from the sun’s harmful UV rays, but also because it can help prevent skin cancer.
The most common form of skin cancer is called basal cell carcinoma and it is caused by exposure to UV radiation.
The best way to protect yourself from this type of cancer is to use sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of at least 15.
This SPF should offer protection against both UVA and UVB rays, which are the two main types of ultraviolet radiation that come from the sun.
Although SPF 15 is enough to provide some protection from the sun, there is a huge difference in quality between the best sunscreens on the market.
That's why we have an article comparing the qualities of the best sunscreens and giving our recommendation.
By reading this article, you can find the sunscreen that best suits your needs and provides the most protection.
Can sun overexposure cause vomiting?
Yes, overexposure to the sun can cause a condition called heatstroke, which can lead to nausea and vomiting.
Heatstroke occurs when the body is unable to regulate its internal temperature, causing it to rise dangerously high.
When this happens, the body begins to shut down, and one of the first symptoms is usually nausea and vomiting.
If you or someone you know starts to experience these symptoms after being in the sun for too long, it's important to seek medical help immediately.
These symptoms include dizziness, headaches, nausea, and confusion.
Can sun overexposure cause headaches?
Yes, sun overexposure can cause headaches. Headaches from sun overexposure are most commonly caused by dehydration, as the body is unable to sweat properly to cool down.
Symptoms of a headache from sun overexposure include throbbing pain, sensitivity to light, and nausea.
If you experience these symptoms after spending time in the sun, it's important to drink plenty of fluids and get out of the heat as soon as possible.
Can sun overexposure cause eczema?
Excessive sun exposure can damage the skin, which may lead to eczema. Eczema is a condition that causes the skin to become dry, itchy, and inflamed.
If you have eczema, you may be more likely to experience a flare-up after spending time in the sun.
To help prevent this, be sure to apply sunscreen before going outside and wear protective clothing if you'll be spending extended periods of time in the sun.
Can sun overexposure cause fever?
Can overexposure to the sun cause a fever? Yes, it is possible for someone to get a fever from being out in the sun too long.
If you are exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays for an extended period of time, your body temperature can rise and you may develop a fever.
Although, it is more likely that you will experience other symptoms of sun overexposure before you develop a fever, such as dizziness, nausea, or headache.
Symptoms of sun overexposure can be mild to severe, and in some cases lead to heat stroke.
Sun overexposure and cataracts
Too much sun exposure can lead to cataracts, a clouding of the eye's lens.
Cataracts can make it harder to see and if left untreated, can eventually cause blindness.
People who are at a higher risk for developing cataracts include those who spend a lot of time outdoors without adequate protection from the sun's harmful rays, as well as people with diabetes or other medical conditions that affect the eyes.
Thanks for Reading!
We hope you found this information on sun safety helpful.
If you enjoyed this article, please consider saving our site, Woman Vitality, to your bookmarks and sharing it with others who might be interested.
We have a wealth of information on all things health and wellness here. Be sure to check out our Health section for more articles just like this one!
References
Grey, H. (2018, July 5). Here’s how much damage a really bad sunburn can do. Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health-news/heres-how-much-damage-a-really-bad-sunburn-can-do
Cadet, J., & Douki, T. (2018). Formation of UV-induced DNA damage contributing to skin cancer development. Photochemical & Photobiological Sciences, 17(12), 1816–1841. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7pp00395a
Ultraviolet radiation. (2021, July 6). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ultraviolet-radiation
NIOSH fast facts: protecting yourself from sun exposure. (2010). https://doi.org/10.26616/nioshpub2010116
Leave A Comment